三种运行方式
不配置unicorn.rb的方式
unicorn_rails -D -l 0.0.0.0:3000 -E development
配置unicorn.rb的方式
unicorn_rails -c /path/to/app/config/unicorn.rb -D -E production
无缝重启方式,如nginx -s reload
kill -USR2 `cat path/to/app/tmp/pids/unicorn.pid`
————————————–
1.在Gemfile中加入
在Gemfile中加入以下一行。
gem 'unicorn'
在命令行中执行以下一行
bundle install
2.listen方式
listen 3000 # listen to port 3000 on all TCP interfaces
listen "127.0.0.1:3000" # listen to port 3000 on the loopback interface
listen "/tmp/.unicorn.sock" # listen on the given Unix domain socket
listen "[::1]:3000" # listen to port 3000 on the IPv6 loopback interface
3.官方最小配置
listen 2007 # by default Unicorn listens on port 8080
worker_processes 2 # this should be >= nr_cpus
pid "/path/to/app/shared/pids/unicorn.pid"
stderr_path "/path/to/app/shared/log/unicorn.log"
stdout_path "/path/to/app/shared/log/unicorn.log"
4.官方最完整配置
# Sample verbose configuration file for Unicorn (not Rack)
#
# This configuration file documents many features of Unicorn
# that may not be needed for some applications. See
# https://bogomips.org/unicorn/examples/unicorn.conf.minimal.rb
# for a much simpler configuration file.
#
# See https://bogomips.org/unicorn/Unicorn/Configurator.html for complete
# documentation.
# Use at least one worker per core if you're on a dedicated server,
# more will usually help for _short_ waits on databases/caches.
worker_processes 4
# Since Unicorn is never exposed to outside clients, it does not need to
# run on the standard HTTP port (80), there is no reason to start Unicorn
# as root unless it's from system init scripts.
# If running the master process as root and the workers as an unprivileged
# user, do this to switch euid/egid in the workers (also chowns logs):
# user "unprivileged_user", "unprivileged_group"
# Help ensure your application will always spawn in the symlinked
# "current" directory that Capistrano sets up.
working_directory "/path/to/app/current" # available in 0.94.0+
# listen on both a Unix domain socket and a TCP port,
# we use a shorter backlog for quicker failover when busy
listen "/path/to/.unicorn.sock", :backlog => 64
listen 8080, :tcp_nopush => true
# nuke workers after 30 seconds instead of 60 seconds (the default)
timeout 30
# feel free to point this anywhere accessible on the filesystem
pid "/path/to/app/shared/pids/unicorn.pid"
# By default, the Unicorn logger will write to stderr.
# Additionally, ome applications/frameworks log to stderr or stdout,
# so prevent them from going to /dev/null when daemonized here:
stderr_path "/path/to/app/shared/log/unicorn.stderr.log"
stdout_path "/path/to/app/shared/log/unicorn.stdout.log"
# combine Ruby 2.0.0+ with "preload_app true" for memory savings
preload_app true
# Enable this flag to have unicorn test client connections by writing the
# beginning of the HTTP headers before calling the application. This
# prevents calling the application for connections that have disconnected
# while queued. This is only guaranteed to detect clients on the same
# host unicorn runs on, and unlikely to detect disconnects even on a
# fast LAN.
check_client_connection false
# local variable to guard against running a hook multiple times
run_once = true
before_fork do |server, worker|
# the following is highly recomended for Rails + "preload_app true"
# as there's no need for the master process to hold a connection
defined?(ActiveRecord::Base) and
ActiveRecord::Base.connection.disconnect!
# Occasionally, it may be necessary to run non-idempotent code in the
# master before forking. Keep in mind the above disconnect! example
# is idempotent and does not need a guard.
if run_once
# do_something_once_here ...
run_once = false # prevent from firing again
end
# The following is only recommended for memory/DB-constrained
# installations. It is not needed if your system can house
# twice as many worker_processes as you have configured.
#
# # This allows a new master process to incrementally
# # phase out the old master process with SIGTTOU to avoid a
# # thundering herd (especially in the "preload_app false" case)
# # when doing a transparent upgrade. The last worker spawned
# # will then kill off the old master process with a SIGQUIT.
# old_pid = "#{server.config[:pid]}.oldbin"
# if old_pid != server.pid
# begin
# sig = (worker.nr + 1) >= server.worker_processes ? :QUIT : :TTOU
# Process.kill(sig, File.read(old_pid).to_i)
# rescue Errno::ENOENT, Errno::ESRCH
# end
# end
#
# Throttle the master from forking too quickly by sleeping. Due
# to the implementation of standard Unix signal handlers, this
# helps (but does not completely) prevent identical, repeated signals
# from being lost when the receiving process is busy.
# sleep 1
end
after_fork do |server, worker|
# per-process listener ports for debugging/admin/migrations
# addr = "127.0.0.1:#{9293 + worker.nr}"
# server.listen(addr, :tries => -1, :delay => 5, :tcp_nopush => true)
# the following is *required* for Rails + "preload_app true",
defined?(ActiveRecord::Base) and
ActiveRecord::Base.establish_connection
# if preload_app is true, then you may also want to check and
# restart any other shared sockets/descriptors such as Memcached,
# and Redis. TokyoCabinet file handles are safe to reuse
# between any number of forked children (assuming your kernel
# correctly implements pread()/pwrite() system calls)
end
5.GitHub配置
# unicorn_rails -c /data/github/current/config/unicorn.rb -E production -D
rails_env = ENV['RAILS_ENV'] || 'production'
# 16 workers and 1 master
worker_processes (rails_env == 'production' ? 16 : 4)
# Load rails+github.git into the master before forking workers
# for super-fast worker spawn times
preload_app true
# Restart any workers that haven't responded in 30 seconds
timeout 30
# Listen on a Unix data socket
listen '/data/github/current/tmp/sockets/unicorn.sock', :backlog => 2048
##
# REE
# http://www.rubyenterpriseedition.com/faq.html#adapt_apps_for_cow
if GC.respond_to?(:copy_on_write_friendly=)
GC.copy_on_write_friendly = true
end
before_fork do |server, worker|
##
# When sent a USR2, Unicorn will suffix its pidfile with .oldbin and
# immediately start loading up a new version of itself (loaded with a new
# version of our app). When this new Unicorn is completely loaded
# it will begin spawning workers. The first worker spawned will check to
# see if an .oldbin pidfile exists. If so, this means we've just booted up
# a new Unicorn and need to tell the old one that it can now die. To do so
# we send it a QUIT.
#
# Using this method we get 0 downtime deploys.
old_pid = RAILS_ROOT + '/tmp/pids/unicorn.pid.oldbin'
if File.exists?(old_pid) && server.pid != old_pid
begin
Process.kill("QUIT", File.read(old_pid).to_i)
rescue Errno::ENOENT, Errno::ESRCH
# someone else did our job for us
end
end
end
after_fork do |server, worker|
##
# Unicorn master loads the app then forks off workers - because of the way
# Unix forking works, we need to make sure we aren't using any of the parent's
# sockets, e.g. db connection
ActiveRecord::Base.establish_connection
CHIMNEY.client.connect_to_server
# Redis and Memcached would go here but their connections are established
# on demand, so the master never opens a socket
##
# Unicorn master is started as root, which is fine, but let's
# drop the workers to git:git
begin
uid, gid = Process.euid, Process.egid
user, group = 'git', 'git'
target_uid = Etc.getpwnam(user).uid
target_gid = Etc.getgrnam(group).gid
worker.tmp.chown(target_uid, target_gid)
if uid != target_uid || gid != target_gid
Process.initgroups(user, target_gid)
Process::GID.change_privilege(target_gid)
Process::UID.change_privilege(target_uid)
end
rescue => e
if RAILS_ENV == 'development'
STDERR.puts "couldn't change user, oh well"
else
raise e
end
end
end
6.自定义配置一
module Rails
class < 64
timeout 30
pid "#{Rails.root}/tmp/pids/unicorn.pid"
stderr_path "#{Rails.root}/log/unicorn.log"
stdout_path "#{Rails.root}/log/unicorn.log"
# combine Ruby 2.0.0dev or REE with "preload_app true" for memory savings
# http://rubyenterpriseedition.com/faq.html#adapt_apps_for_cow
preload_app true
GC.respond_to?(:copy_on_write_friendly=) and
GC.copy_on_write_friendly = true
check_client_connection false
before_fork do |server, worker|
# the following is highly recomended for Rails + "preload_app true"
# as there's no need for the master process to hold a connection
defined?(ActiveRecord::Base) and
ActiveRecord::Base.connection.disconnect!
old_pid = "#{server.config[:pid]}.oldbin"
if File.exists?(old_pid) && old_pid != server.pid
begin
sig = (worker.nr + 1) >= server.worker_processes ? :QUIT : :TTOU
Process.kill(sig, File.read(old_pid).to_i)
rescue Errno::ENOENT, Errno::ESRCH
end
end
# Throttle the master from forking too quickly by sleeping. Due
# to the implementation of standard Unix signal handlers, this
# helps (but does not completely) prevent identical, repeated signals
# from being lost when the receiving process is busy.
sleep 1
end
after_fork do |server, worker|
# the following is *required* for Rails + "preload_app true",
defined?(ActiveRecord::Base) and
ActiveRecord::Base.establish_connection
# if preload_app is true, then you may also want to check and
# restart any other shared sockets/descriptors such as Memcached,
# and Redis. TokyoCabinet file handles are safe to reuse
# between any number of forked children (assuming your kernel
# correctly implements pread()/pwrite() system calls)
end
7.自定义配置二
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
user("menxu","menxu")
root_path = File.expand_path '../', File.dirname(__FILE__)
#log
log_file = root_path + '/log/unicorn.log'
err_log = root_path + '/log/unicorn_error.log'
# process
pid_file = '/tmp/unicorn_padrino.pid'
old_pid = pid_file + '.oldbin'
#thron
socket_file = '/tmp/unicorn_padrino.sock'
worker_processes 2
working_directory root_path
timeout 30
#listen
listen 8080, tcp_nopush: false
listen socket_file, backlog: 1024
pid pid_file
stderr_path err_log
stdout_path log_file
preload_app true
before_exec do |server|
ENV['BUNDLE_GEMFILE'] = root_path + '/Gemfile'
end
before_fork do |server, worker|
if File.exists?(old_pid) && server.pid != old_pid
begin
Process.kill('QUIT', File.read(old_pid).to_i)
rescue Errno::ENOENT, Errno::ESRCH
puts "Send 'QUIT' signal to unicorn error!"
end
end
end
8.nginx.conf的配置
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 0;
upstream app_server {
# fail_timeout=0 means we always retry an upstream even if it failed
# to return a good HTTP response (in case the Unicorn master nukes a
# single worker for timing out).
# for UNIX domain socket setups:
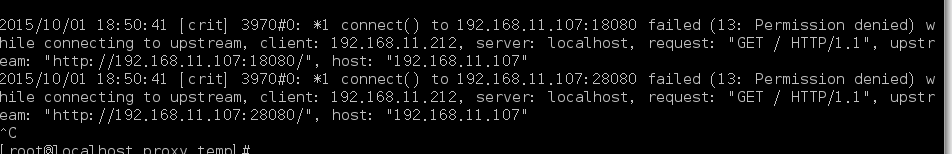
server unix: /path/to/app/tmp/sockets/socket fail_timeout=0;
}
server {
listen 8080 default;
return 403;
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name www.explame.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://app_server;
}
# Rails error pages
error_page 500 502 503 504 /500.html;
location = /500.html {
root /path/to/app/current/public;
}
}
}