@Resource的作用相当于@Autowired,只不过@Autowired按byType自动注入,而@Resource默认按 byName自动注入罢了。@Resource有两个属性是比较重要的,分是name和type,Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,而type属性则解析为bean的类型。所以如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略。如果既不指定name也不指定type属性,这时将通过反射机制使用byName自动注入策略。
@Resource装配顺序
1. 如果同时指定了name和type,则从Spring上下文中找到唯一匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
2. 如果指定了name,则从上下文中查找名称(id)匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
3. 如果指定了type,则从上下文中找到类型匹配的唯一bean进行装配,找不到或者找到多个,都会抛出异常
4. 如果既没有指定name,又没有指定type,则自动按照byName方式进行装配;如果没有匹配,则回退为一个原始类型进行匹配,如果匹配则自动装配;
分类目录归档:Java开发
Spring库的Repository
spring-milestone
https://repo.spring.io/libs-milestone
true repository.spring.snapshot
Spring Snapshot Repository
http://repo.spring.io/snapshot
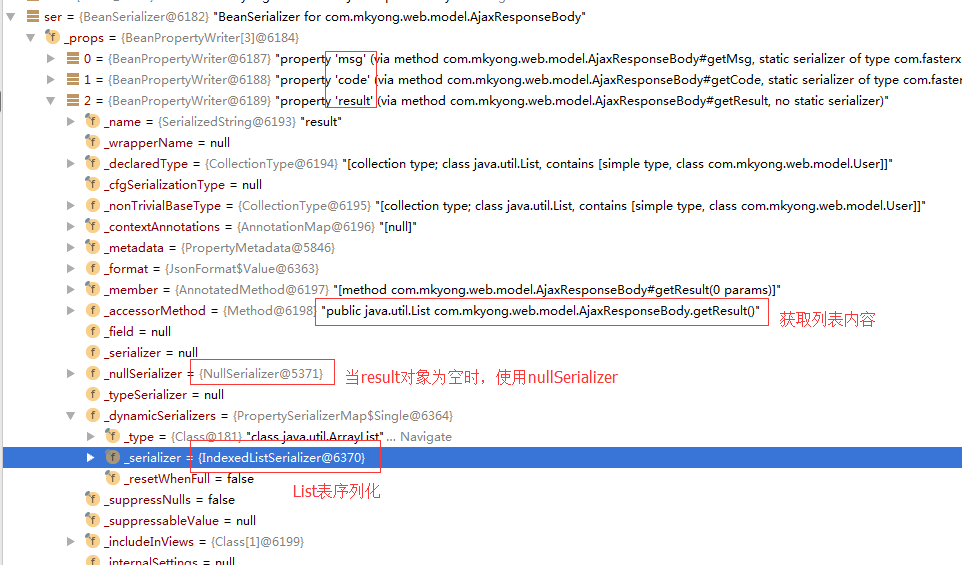
fastxml.json的序列化
专门分析一下fastxml.json的序列化,偶有所得,截图如下:

另一个示例
public class User {
public interface WithoutPasswordView {};
public interface WithPasswordView extends WithoutPasswordView {};
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@JsonView(WithoutPasswordView.class)
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
@JsonView(WithPasswordView.class)
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//创建对象
User user = new User("isea533","123456");
//序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
objectMapper.writerWithView(User.WithoutPasswordView.class).writeValue(bos, user);
System.out.println(bos.toString());
bos.reset();
objectMapper.writerWithView(User.WithPasswordView.class).writeValue(bos, user);
System.out.println(bos.toString());
}
}
输出结果
{"username":"isea533"}
{"username":"isea533","password":"123456"}
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-core
${jackson.version}
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
${jackson.version}
@EnableWebMvc在做什么?
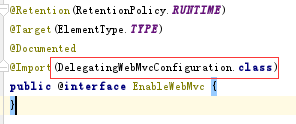
如红框所示,在构建beanmap的列表过程中,会主动加载该类,构建默认bean列表。在DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration中,会建立以下默认bean列表。
HandlerMapping:
Bean: requestMappingHandlerMapping
Bean: viewControllerHandlerMapping
Bean: beanNameHandlerMapping
Bean: resourceHandlerMapping
Bean: defaultServletHandlerMapping
HandlerAdapter:
Bean: requestMappingHandlerAdapter
Bean: httpRequestHandlerAdapter
Bean: simpleControllerHandlerAdapter
ExceptionResolver
Bean: handlerExceptionResolver
Other:
Bean: mvcConversionService
Bean: mvcValidator
以上bean也是可以通过基于WebMvcConfigurationSupport派生新配置类来进行高级的修改上述bean的配置。
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
//@ComponentScan(basePackages = "web.api.module", useDefaultFilters = false, includeFilters = {
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = {Controller.class})
//})
@ComponentScan("web.api.module.*")
@Import({ SecurityConfig.class })
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(WebConfig.class);
public WebConfig(){
}
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
logger.info("ViewResolver");
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
logger.info("MessageSource");
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("config.messages.messages");
return messageSource;
}
@Bean
public HandlerAdapter servletHandlerAdapter(){
logger.info("HandlerAdapter");
return new SimpleServletHandlerAdapter();
}
@Bean
public LocaleChangeInterceptor localeChangeInterceptor(){
logger.info("LocaleChangeInterceptor");
return new LocaleChangeInterceptor();
}
@Bean(name="localeResolver")
public CookieLocaleResolver cookieLocaleResolver(){
logger.info("CookieLocaleResolver");
return new CookieLocaleResolver();
}
@Bean
public CsrfIntercepter initializingCsrfInterceptor(){
logger.info("CsrfIntercepter");
return new CsrfIntercepter();
}
/**
* 描述 : <注册自定义拦截器>.
*
<使用方法说明>
* @return
*/
@Bean
public LoginCheckInterceptor initializingInterceptor(){
logger.info("LoginCheckInterceptor");
return new LoginCheckInterceptor();
}
/**
* 描述 : .
*
<这个比较奇怪,理论上应该是不需要的>
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
logger.info("RequestMappingHandlerMapping");
return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping();
}
@Override
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logger.info("addInterceptors start");
registry.addInterceptor(localeChangeInterceptor());
registry.addInterceptor(initializingInterceptor());
// registry.addInterceptor(initializingCsrfInterceptor());
logger.info("addInterceptors end");
}
@Bean
public HandlerMapping resourceHandlerMapping() {
logger.info("HandlerMapping");
return super.resourceHandlerMapping();
}
/**
* 描述 : <资源访问处理器>.
*
<可以在jsp中使用/static/**的方式访问/WEB-INF/static/下的内容>
* @param registry
*/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
logger.info("addResourceHandlers");
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("/WEB-INF/static/");
}
/**
* 描述 : <异常处理器>.
*
<系统运行时遇到指定的异常将会跳转到指定的页面>
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="exceptionResolver")
public ExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver(){
logger.info("ExceptionResolver");
ExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver= new ExceptionResolver();
simpleMappingExceptionResolver.setDefaultErrorView("common_error");
simpleMappingExceptionResolver.setExceptionAttribute("exception");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("java.lang.RuntimeException", "common_error");
simpleMappingExceptionResolver.setExceptionMappings(properties);
return simpleMappingExceptionResolver;
}
/**
* 描述 : .
*
<这个比较奇怪,理论上应该是不需要的>
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter() {
logger.info("RequestMappingHandlerAdapter");
return super.requestMappingHandlerAdapter();
}
@Override
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer() {
logger.info("ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer");
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer initializer = super.getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer();
return initializer;
}
}
Hibernate的Entity等同于YII的Model
每个Entity是数据表的一行记录。
public class Main {
private static final SessionFactory ourSessionFactory;
static {
try {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//"hibernate.cfg.xml"
configuration.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
ourSessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static Session getSession() throws HibernateException {
return ourSessionFactory.openSession();
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
final Session session = getSession();
try {
System.out.println("querying all the managed entities...");
final Map metadataMap = session.getSessionFactory().getAllClassMetadata();
for (Object key : metadataMap.keySet()) {
final ClassMetadata classMetadata = (ClassMetadata) metadataMap.get(key);
final String entityName = classMetadata.getEntityName();
final Query query = session.createQuery("from " + entityName);
System.out.println("executing: " + query.getQueryString());
List
CGLib代理模式
CGLib是采用字节码方式注入到程序中的,这种方式就像C++中的Detour库注入汇编代码,从而达到监控函数运行的效果。由于CGLib是采用继承的关系,故它不能代理final类。以下是测试代码。
CglibProxy.java
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CglibProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
// private static CglibProxy proxy = new CglibProxy();
private Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
public Object getProxy(Class clazz) {
enhancer.setSuperclass(clazz);// 设置需要创建子类的类
enhancer.setCallback(this);
return enhancer.create();// 通过字节码技术动态创建子类实例
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object arg0, Method arg1, Object[] arg2,
MethodProxy arg3) throws Throwable {
Object result = arg3.invokeSuper(arg0, arg2);
return result;
}
}
public class UserServiceImpl{
public void removeUser(int userId) {
System.out.println("模拟删除用户:" + userId);
}
public void addUser(int userId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CglibProxy proxy = new CglibProxy();
UserServiceImpl userService =(UserServiceImpl)proxy.getProxy(UserServiceImpl.class);
userService.removeUser(7);
}
}
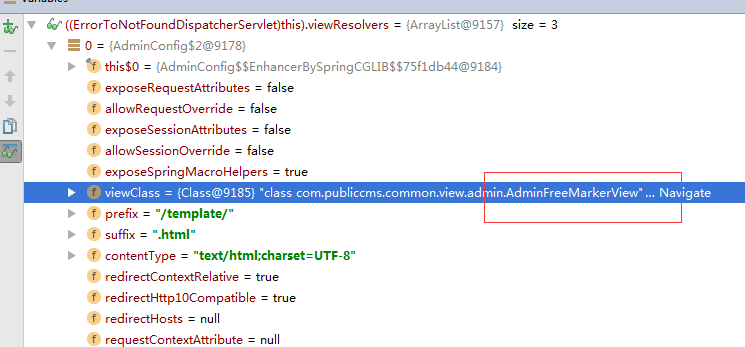
freemarker在Spring中的View渲染关建过程
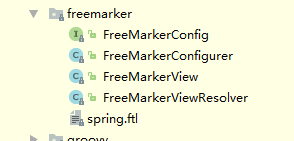
1.Spring已经集成了FreeMarker的相关组件,保存在org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker之下,如下图所示:

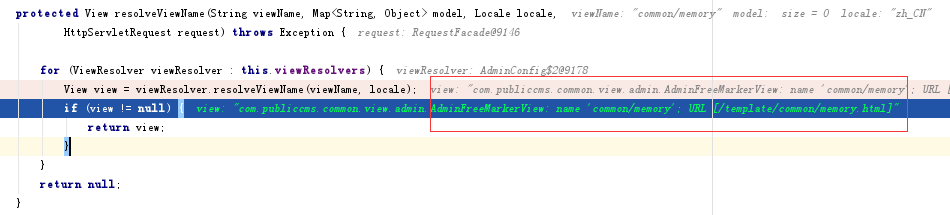
2.在RequestMapping的处理后,是如何关联freemarker视图处理呢?关键在DispatcherServlet类中。
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map model, Locale locale,
HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
//返回FreeMarkerView对象,保存到view中。
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
View view;
//从requestmapping处理函数返回来后,根据viewname,即相对路径,获取FreeMarkerView对象。
view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
3.FreeMarkerView负责freemarker的渲染,其关键函数如下:
protected Configuration getConfiguration() {
//该configuration对象是FreeMarkerConfigurer对象,而后续渲染所需要的资源将是从该configure中获取。
//该configuration是FreeMarkerView的成员。
return this.configuration;
}
protected Template getTemplate(String name, Locale locale) throws IOException {
//在getTimplate的过程中,configuration对象,也被传递到Template中,方便后续
//构建Environment对象使用如template.getConfiguration();
return (getEncoding() != null ?
getConfiguration().getTemplate(name, locale, getEncoding()) :
getConfiguration().getTemplate(name, locale));
}
protected Template getTemplate(Locale locale) throws IOException {
//通过getUrl获
return getTemplate(getUrl(), locale);
}
protected void doRender(Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
SimpleHash fmModel = buildTemplateModel(model, request, response);
Locale locale = RequestContextUtils.getLocale(request);
processTemplate(getTemplate(locale), fmModel, response);
}
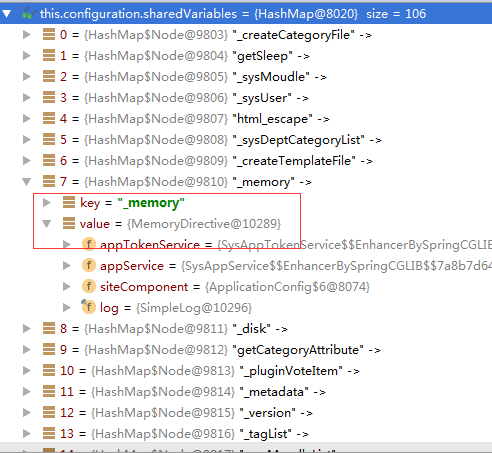
4.它是如何把每个freemarker的指令存放到configure中的呢?如下:
@Autowired(required = false)
private void TemplateComponent::setFreeMarkerConfigurer(FreeMarkerConfigurer freeMarkerConfigurer,
Map taskDirectiveMap,
Map templateDirectiveMap, Map methodMap)
throws IOException, TemplateModelException {
Map freemarkerVariables = new HashMap();
adminConfiguration = freeMarkerConfigurer.getConfiguration();
log.info("Freemarker directives and methods Handler started");
//根据自定义命名规则,建立命名列表。
StringBuffer templateDirectives = new StringBuffer();
for (Entry entry : templateDirectiveMap.entrySet()) {
String directiveName = directivePrefix
+ uncapitalize(entry.getKey().replaceAll(directiveRemoveRegex, BLANK));
freemarkerVariables.put(directiveName, entry.getValue());
if (0 != templateDirectives.length()) {
templateDirectives.append(COMMA_DELIMITED);
}
templateDirectives.append(directiveName);
}
StringBuffer methods = new StringBuffer();
for (Entry entry : methodMap.entrySet()) {
String methodName = uncapitalize(entry.getKey().replaceAll(methodRemoveRegex, BLANK));
freemarkerVariables.put(methodName, entry.getValue());
if (0 != methods.length()) {
methods.append(COMMA_DELIMITED);
}
methods.append(methodName);
}
//将命名列表和bean对象一一对应地保存到configuration中。
adminConfiguration.setAllSharedVariables(new SimpleHash(freemarkerVariables, adminConfiguration.getObjectWrapper()));
}
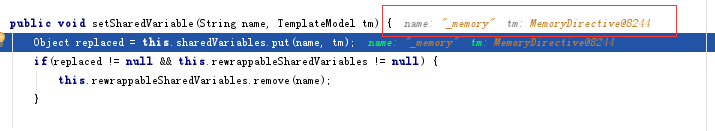
public void Configuration::setAllSharedVariables(TemplateHashModelEx hash) throws TemplateModelException {
TemplateModelIterator keys = hash.keys().iterator();
TemplateModelIterator values = hash.values().iterator();
while(keys.hasNext()) {
//逐个将自定义命令和对应的bean实例,以一一对应方式保存到Configure的sharedVariable成员中。
//_memory与MemoryDirective
this.setSharedVariable(((TemplateScalarModel)keys.next()).getAsString(), values.next());
}
}
5.它是如何处理模板呢?
protected void FreeMarkerView::processTemplate(Template template, SimpleHash model, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, TemplateException {
template.process(model, response.getWriter());
}
public Template::Environment(Template template, TemplateHashModel rootDataModel, Writer out) {
super(template);
//模板中取出configuration,configuration已经包括各种模板扩展的自定义指令。
this.configuration = template.getConfiguration();
this.globalNamespace = new Environment.Namespace((Template)null);
this.currentNamespace = this.mainNamespace = new Environment.Namespace(template);
this.out = out;
this.rootDataModel = rootDataModel;
//分析模板结构,构建出指令树。
this.importMacros(template);
}
public Environment Template::createProcessingEnvironment(Object dataModel, Writer out, ObjectWrapper wrapper) throws TemplateException, IOException {
return new Environment(this, (TemplateHashModel)dataModelHash, out);
}
//递归式,处理每一个自定义指令。
void Environment::visit(TemplateElement element) throws IOException, TemplateException {
this.pushElement(element);
try {
//element.accept就是自定义指令的执行过程,如它会调用MemoryDirective。
TemplateElement[] te = element.accept(this);
if(te != null) {
TemplateElement[] var3 = te;
int var4 = te.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
TemplateElement el = var3[var5];
if(el == null) {
break;
}
this.visit(el);
}
}
} catch (TemplateException var10) {
this.handleTemplateException(var10);
} finally {
this.popElement();
}
}
//从Root节点开始,处理自定义模板指令。
public void Environment::process() throws TemplateException, IOException {
this.visit(this.getTemplate().getRootTreeNode());
}
public void Template::process(Object dataModel, Writer out) throws TemplateException, IOException {
//this.createProcessingEnvironment(dataModel, out, (ObjectWrapper)null),返回的是Environment对象。
this.createProcessingEnvironment(dataModel, out, (ObjectWrapper)null).process();
}
6.每个模块执行过程:element.accept(this))最终会调用以下代码。
@Component
public class MemoryDirective extends AbstractTemplateDirective {
@Override
public void execute(RenderHandler handler) throws IOException, Exception {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
handler.put("freeMemory", runtime.freeMemory());
handler.put("totalMemory", runtime.totalMemory());
handler.put("maxMemory", runtime.maxMemory());
handler.render();
}
}
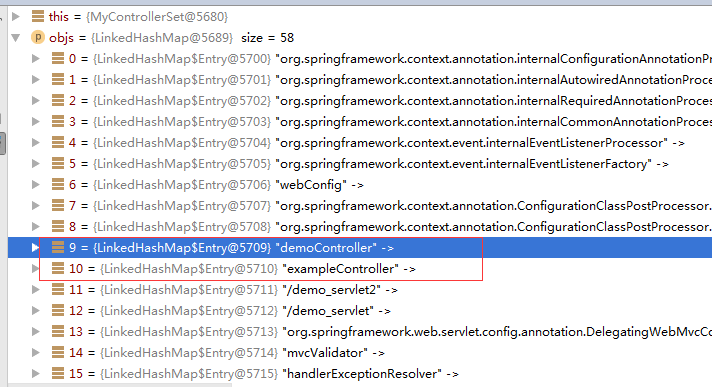
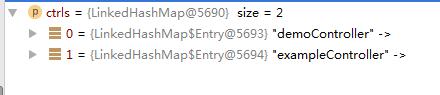
在Spring中获取当前所有beanmap和某特定beanmap记录集
@Component
public class MyControllerSet {
@Autowired()
public void setAllBeanObject2(Map objs, Map ctrls)
{
//objs和ctrls会分别返回所以的beanmap对象和BaseControler对象,看后图示。
int i = 0;
}
}
public abstract class BaseControler {
}
-------------------------------
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController extends BaseControler{
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(DemoController.class);
}
--------------------------------
@Controller
public class ExampleController extends BaseControler{
}
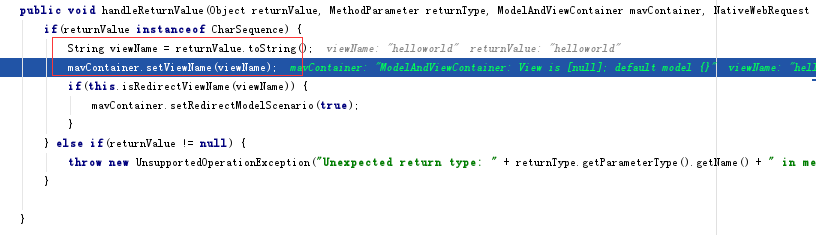
RequestMapping直接返回字符串时,是被默认当作路径使用。
RequestMapping直接返回字符串时,是被默认当作路径使用。
带@ResponseBody注解除外。
@RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/hello**" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String welcome() {
return "helloworld";
}
Spring免配置启动过程
1.启动时,tomcat调用SpringServletContainerInitializer的onStartup函数,传当前可被调用的启动类。
public void onStartup(Set> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext){
for (Class waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) waiClass.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
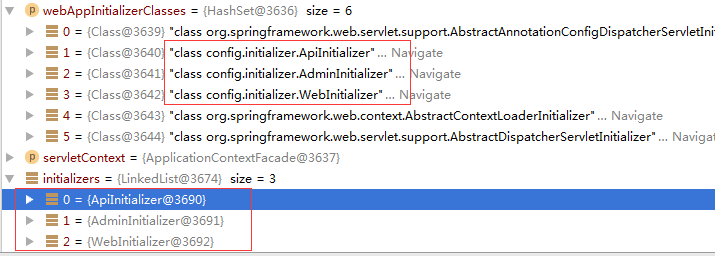
2.如果有RootConfigClasses配置,则会注册ContextLoaderListener,如AdminInitializer类,多个AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer中,有且仅有一个可以配置RootConfigClasses,其余的如果配置了则会抛异常。
AdminInitializer类的Root配置。
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { ApplicationConfig.class };
}
WebInitializer和ApiInitializer都是返回null.
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
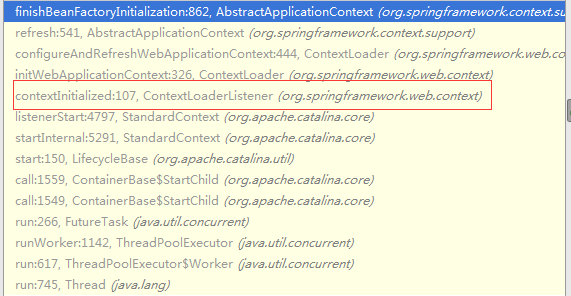
//在onStartUp函数结束后,Tomcat会主动调ContextLoaderListener类的contextInitialized函数。
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
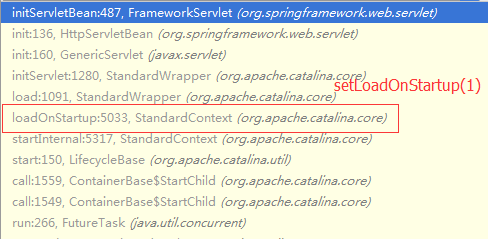
3.创建DispatcherServlet对象并注册。setLoadOnStartup(1)参数为1,表示Tomcat在执行完ContextLoaderListener的相关beanmap处理后,将依次调用Servlet的loadOnStartup函数。
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
//setLoadOnStartup(1),将继ContextLoaderListener之后被调用。
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
}
4.经上述三个步骤,程序将会返回至Tomcat内部,至此完成了onStartup的调用。该过程Tomcat只是完成了HttpServlet的注册和ContextLoaderListener的注册,而beanFactory扫描Controller/Service/Conponent/Repository注解建立beanmap及相应的单实例,以及涉及到的Controller的成员注入,仍没有开始。
5.因为是异步调用的关系,Tomcat接着调用ContextLoaderListener完成WebApplicationContext配置。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
//这段异常,表示有且只有一个getRootConfigClasses函数能被返回全局配置。其它均会共享使用它的全局beanmap。
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
try {
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
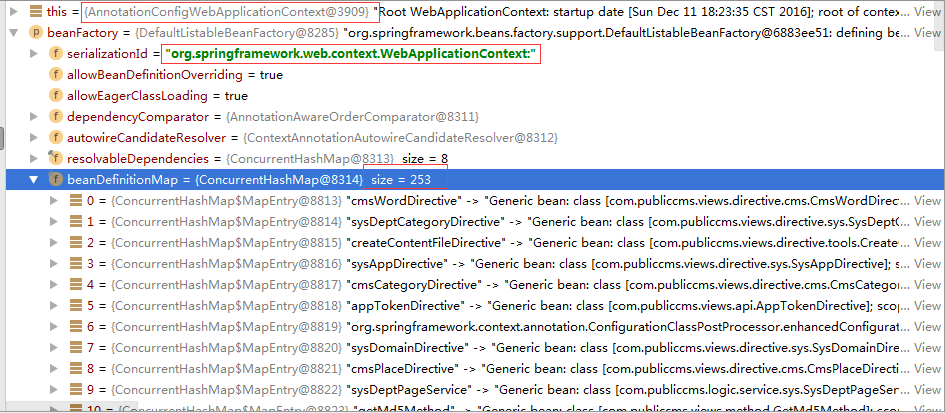
//将扫描指定的目录下的所有Component组件,并形成beanmap,并依据autowired注解自动完成每一个bean对象的单实例化。
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//保存到servletContext的属性中,方便后续DispatcherContext的bean调用及合并。
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
6.因为setLoadOnStartup的关系,Tomcat调用Servlet的bean初始化。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//此处是initWebAppicationContext与5步骤中的initWebApplicationContext不是同一个函数。
//但函数的用途是一致的,都是用于依据bean配置构建beanmap及单实例化。
//此处的配置文件是由getServletConfigClasses提供。
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取getRootConfigClasses设置的全局配置,由此可知每个DispatchServlet对象均会继承全局Root配置。
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//和Root配置一样的搜索过程,建立DispatchServlet的beanmap列表。
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
return wac;
}
7.到这步骤,已经完成Spring的初始化进程了,如果不报错的话,应该可以访问网站了。